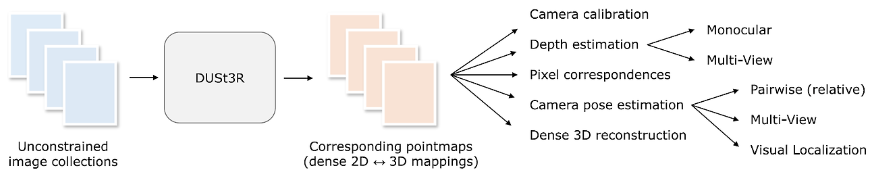
DUSt3R
Geometric 3D Vision Made Easy (CVPR 2024)
DUSt3R - Geometric 3D Vision Made Easy (CVPR 2024)
Shuzhe Wang, Vincent Leroy, Yohann Cabon, Boris Chidlovskii, Jerome Revaud
paper :
https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.14132
project website :
https://europe.naverlabs.com/research/publications/dust3r-geometric-3d-vision-made-easy/
code :
https://github.com/naver/dust3r
reference :
https://xoft.tistory.com/83
Contribution
-
MVS(Multi-View Stereo) 분야에서는 일반적으로 camera param.를 알아야 해서
bundle adjustment 등 최적화 과정을 거치는 SfM(Structure from Motion)을 사용해서 camera param. estimaton을 하지만
이는 많은 연산 필요 -
DUSt3R :
- 많은 연산을 필요로 하는
SfM 생략(pose-free) - transformer 기반으로
2D(img pixel)-to-3D(point map)mapping 예측하여
regression-based3D recon. 수행 - 2-view transformer 이용하여 self-supervised regression
- 1번 view를 기준으로 2번 view의 3D points를
상대적으로 align하므로
(3D point의 절대적인 위치를 추정하는 게 아니므로)
intrinsic/extrinsiccamera param. 몰라도ok - predicted pointmap 기반으로
intrinsic/extrinsic camera param. 추정 가능
- 많은 연산을 필요로 하는
Algorithm
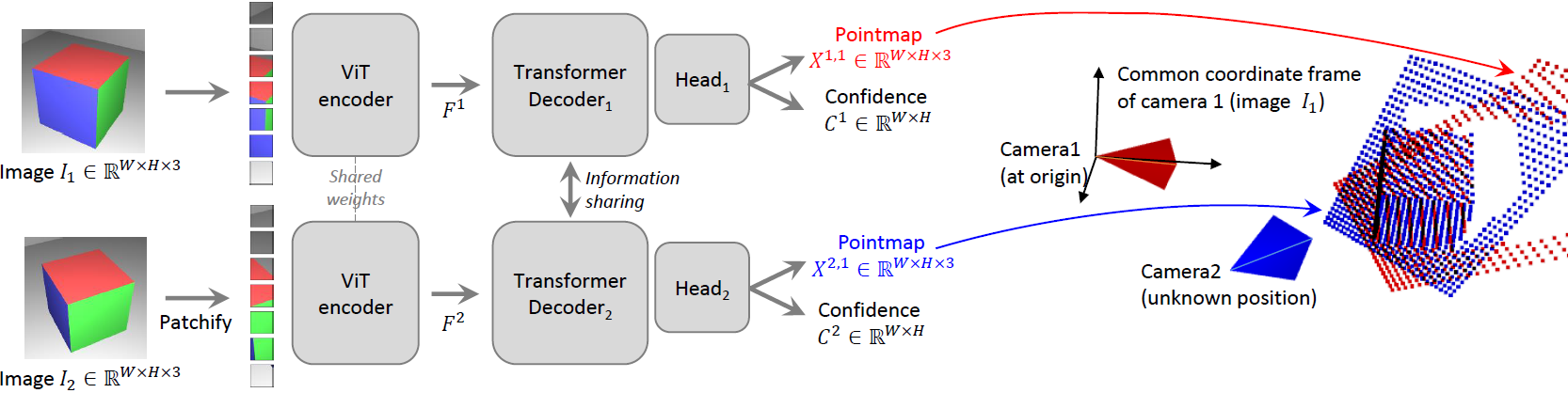
- Algorithm :
shared-weight 및 cross-attention으로 relevant relation을 학습함으로써
(view A의 pcd의 빈 부분을 view B의 pcd 도움으로 채우고, vice versa)
3D geometry를 학습할 수 있음!- Step 1) input
image 2장 - Step 2) ViT encoder
두 images의 feature 비교하기 위해
Siamese(shared weight) 구조 사용 - Step 3) Transformer decoder
두 features의 관계를 학습하여
aligned pointmap 만들기 위해
self-attention and cross-attention수행 - Step 4) Head output
per-pixelPointmap\(X_{i}^{v, 1} \in R^{W \times H \times 3}\)
and
per-pixelConfidencescore \(C_{i}^{v, 1} \in R^{W \times H}\)
(이 때, 두 Pointmap 모두첫 번째 view(frame)의 coordinate에 aligned)
- Step 1) input
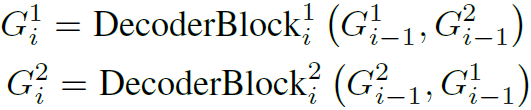
1번 camera : base view, 2번 camera : reference view
\(G_{i}^{1}\) : 1번 view feature의 Transformer Decoder에서 \(i\)-th Block
\(G_{i}^{2}\) : 2번 view feature의 Transformer Decoder에서 \(i\)-th Block
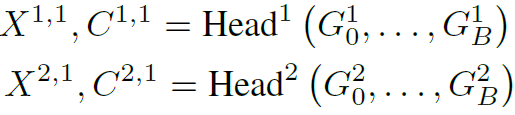
-
Pointmap :
\(X^{1, 1}\) : 1번 view-point를 중심좌표계로 두고 1번 view에서 보이는 3D point 좌표
\(X^{2, 1}\) : 1번 view-point를 중심좌표계로 두고 2번 view에서 보이는 3D point 좌표 - Confidence score :
\(C_{i}^{v, 1}\) : 1번 view 시점을 기준으로 \(v\) 번 view에서 보이는 \(i\)-th 3D point의 confidence score- 물체인 부분에서는 3D point를 비교적 정확히 예측할 수 있으므로 confidence가 높고,
하늘 또는 반투명인 부분에서는 3D point를 정확하게 예측할 수 없으므로 confidence가 낮게 나옴 - \(C_{i}^{v, 1} = 1 + \text{exp}(\tilde C_{i}^{v, 1}) \gt 1\) 로 설정하여
하나의 view에만 존재해서 추정하기 어려운 3D point의 경우에는 extrapolate할 수 있도록???
- 물체인 부분에서는 3D point를 비교적 정확히 예측할 수 있으므로 confidence가 높고,
- 1번 view를 기준으로 2번 view의 3D points를
상대적으로 align하므로
3D point의절대적인 위치를 추정하는 게 아니므로
intrinsic/extrinsiccamera param. 몰라도ok
Loss
- regression loss :
\(L_{regr} (v, i) = \| \frac{1}{z} X_{i}^{v, 1} - \frac{1}{\bar z} \bar X_{i}^{v, 1} \|\)- \(i\) : each point, \(v\) : each view
- \(z = \text{norm}(X^{1, 1}, X^{2, 1})\) : averaged depth of prediction point
- \(\bar z = \text{norm}(\bar X^{1, 1}, \bar X^{2, 1})\) : averaged depth of GT point
-
$$\text{norm}(X^{1, 1}, X^{2, 1}) = \frac{1}{ D^{1} + D^{2} } \sum_{v \in { 1, 2 }} \sum_{i \in D^{v}} | X_{i}^{v, 1} |$$ : 모든 depth 값에 대한 평균
- final loss :
\(L_{conf} = \sum_{v \in \{ 1, 2 \}} \sum_{i \in D^{v}} C_{i}^{v, 1} L_{regr}(v, i) - \alpha \text{log} C_{i}^{v, 1}\)- \(C_{i}^{v, 1} L_{regr}(v, i)\) :
confidence가 큰(확실한) point에서는 GT와의regression loss\(L_{regr}\) 가 더작도록 - \(- \alpha \text{log} C_{i}^{v, 1}\) : regularization term
confidence\(C_{i}^{v, 1}\) 값이너무 작아지지 않도록
- \(C_{i}^{v, 1} L_{regr}(v, i)\) :
Experiments
- Model
CroCo pre-trained model 사용하여 weight initialization- encoder : ViT-Large
- decoder : ViT-Base
- head : DPT (ViT를 Depth Estimation에 적용한 연구)
Downstream - stereo pixel matching
- 2개의 image에 대한 3D pointmap을 겹쳤을 때 align되도록
3D 공간 상에서 pixel correspondence를 찾음- \(X^{2, k}\) 중에 3D point \(X_{i}^{1, k}\) 와 가장 가까운 3D point가 \(X_{j}^{2, k}\) 이고,
동시에 \(X^{1, k}\) 중에 3D point \(X_{j}^{2, k}\) 와 가장 가까운 3D point가 \(X_{i}^{1, k}\) 일 때
두 pixel \(i, j\) 사이에 correspondence 있다고 함 - 모든 pixel에 대해 correspondence가 생기지는 않음
- \(X^{2, k}\) 중에 3D point \(X_{i}^{1, k}\) 와 가장 가까운 3D point가 \(X_{j}^{2, k}\) 이고,
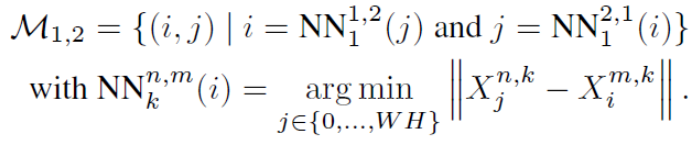
Downstream - camera intrinsic estimation
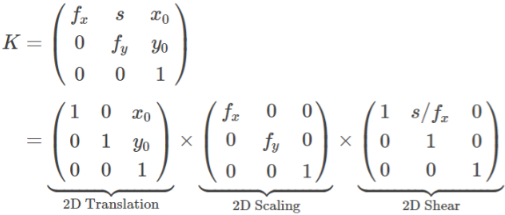
- camera intrinsic :
camera intrinsic을 추정한다는 것은
보통 sclaing matrix, 즉 focal length를 추정한다는 얘기임- 2D translation : principal point의 위치
(보통 이미지의 정가운데) - 2D shear : 카메라가 기울어진 정도
(보통 카메라는 기울어져 있지 않으므로 shear matrix는 고려 X) - 2D scaling : focal length
- 2D translation : principal point의 위치
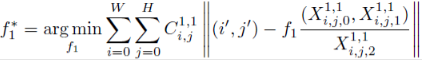
- 위의 수식 설명 :
- focal length는 3D point를 2D image plane으로 projection시킬 때 사용됨
Weiszfeld algorithm을 이용해서 2D 상에서 위의 반복 최적화 문제를 풀면
해당 optimalfocal length를 가질 때2D image와 3D point가 align됨 - camera-coordinate에서 최적화 수행
where pixel-coordinate : 2D \((i, j) \in ([0, W], [0, H])\) (좌상단이 원점)
where camera-coordinate : 2D $$i^{‘}, j^{‘} \in ([-\frac{W}{2}, \frac{W}{2}], [-\frac{H}{2}, \frac{H}{2}]) (정중앙이 원점)
where world-coordinate : 3D
- focal length는 3D point를 2D image plane으로 projection시킬 때 사용됨
Downstream - camera extrinsic estimation
- Relative Pose Estimation :
- 방법 1)
위에서 언급한 2D pixel matching과 intrinsic estimation을 수행한 뒤
Eight-Point algorithm 등 이용해서
epipolar(essential) matrix와 relative pose를 추정 - 방법 2)
서로 다른 view 시점에서 보이는 3D pointmap이 동일해지도록
SVD-based procrustes alignment algorithm 이용해 3D 상에서 반복 최적화 문제를 풀어서
optimal rotation matrix \(R\), translation vector \(t\), scale factor \(\sigma\) 추정- procrustes alignment algorithm은 noise 및 outlier에 민감하므로
주어진 3D point와 corresponding 2D point를 바탕으로 camera pose를 추정하는 PnP algorithm과
random sampling 방식의 RANSAC (Random Sample Consensus) algorithm 이용해서 위 수식의 해를 찾음
?????
- procrustes alignment algorithm은 noise 및 outlier에 민감하므로
- 방법 1)
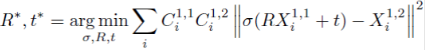
- Absolute Pose Estimation (visual localization) :
- 방법 1)
위에서 언급한 2D pixel matching과 instrinsic estimation을 수행한 뒤
PnP RANSAC algorithm 이용해서 optimal rotation matrix 및 translation vector 추정 - 방법 2)
GT pointmap을 이용
즉, 위에서 언급한 Relative Pose Estimation을 수행할 때
해당 GT로 scale을 맞춰서 진행
- 방법 1)
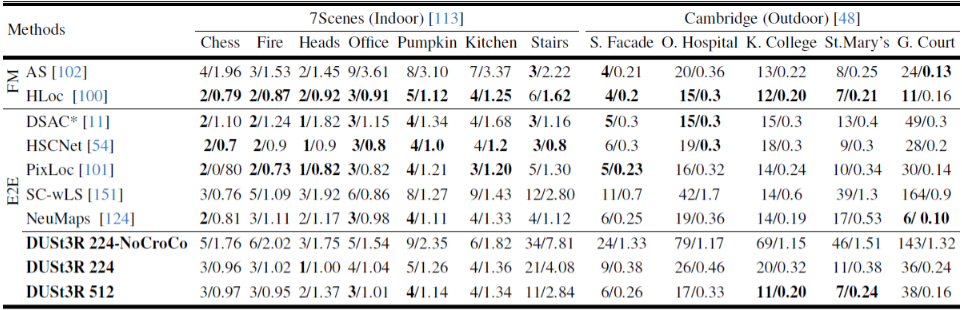
- Experiment on Absolute Pose Estimation :
- test dataset :
7Scenes, Cambridge Landmark
(training에 사용되지 않은 dataset) - 각 값은 translation error (cm) / rotation error (degree)
- 방식 :
query image가 주어지면
가장 관련 있는 image를 test dataset에서 찾아
2개 image 간의 pixel을 matching하여 Absolute Camera Pose 계산
(근데 query image와 test dataset image 간의 GT camera pose가 존재하나???) - 비교 :
FM(feature matching 기법), E2E(end-to-end learning 기법)과 비교했을 때
SOTA 성능은 아니지만
DUSt3R이 visual localization을 목적으로 학습되지 않았는데도 오차가 작다는 것을 확인할 수 있음
- test dataset :
Downstream - Global Alignment
- Global Alignment :
3장 이상의 images로부터 예측한 Pointmap을 3D space에서 align하는 방법- 여러 장의 images를 다루기 위해
Graph만듦 (각 image가 vertex이고, 같은 visual contents를 공유하고 있으면 edge) - DUSt3R 이용해서
모든 edge pair에 대해 Pointmap \(X_{i}^{v, 1} \in R^{W \times H \times 3}\) 과 Confidence score \(C_{i}^{v, 1} \in R^{W \times H}\) 계산 - 여러 장의 images로 3D 상에서 반복 최적화 문제 풀어서
여러 장의 images로부터 얻은 Pointmap들이 3D 상에서 align되도록 함
- 여러 장의 images를 다루기 위해
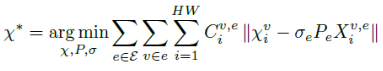
- 위의 수식 설명 :
3D 상에서 위의 반복 최적화 문제를 풀어서
optimal \(\xi_{i}^{v}, \sigma_{e}, P_{e}\) 얻으면
\(N\) 개의 images로 얻은 \(N\) 개의3D Pointmap을 align하여
Global pointmap을 얻을 수 있음
코드 : Code- \(C_{i}^{v, e}\) : confidence score from DUSt3R prediction
(image \(e\) 의 view 시점을 기준으로, image \(v\) view에서 보이는 \(i\)-th pixel에 대응되는 값) - \(X_{i}^{v, e}\) : pointmap from DUSt3R prediction
- \(\xi_{i}^{v}\) : global pointmap in world-coordinate
- \(\sigma_{e}\) : edge로 연결되어 있는 2개 images 간의 scale factor
(0이 되는 것을 방지하기 위해 \(\prod_{e} \sigma_{e} = 1\) 로 설계) - \(P_{e}\) : edge로 연결되어 있는 2개 images 간의 relative pose
- \(C_{i}^{v, e}\) : confidence score from DUSt3R prediction
- 위의 방법은
전통적인 SfM bundle adjustment 방법과 달리
빠르고 단순하게 regression(gradient descent)-based로 반복 최적화 문제 풂- bundle adjustment :
2D reprojection error 최소화 - 본 논문 :
2D reprojection 뿐만 아니라 3D projection error을 같이 최소화
- bundle adjustment :
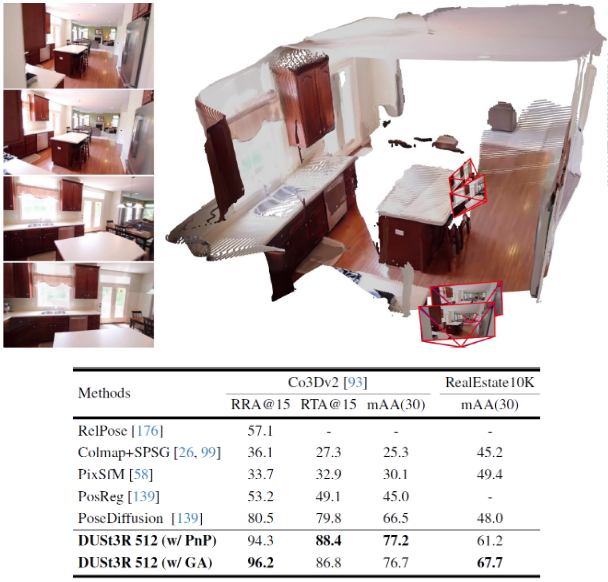
Downstream - Depth Estimation
- Monocular Depth Estimation
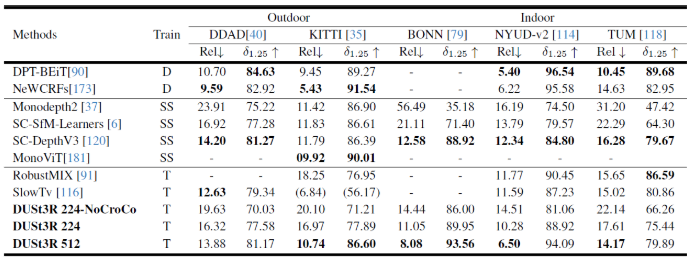
- Multi-view Depth Estimation
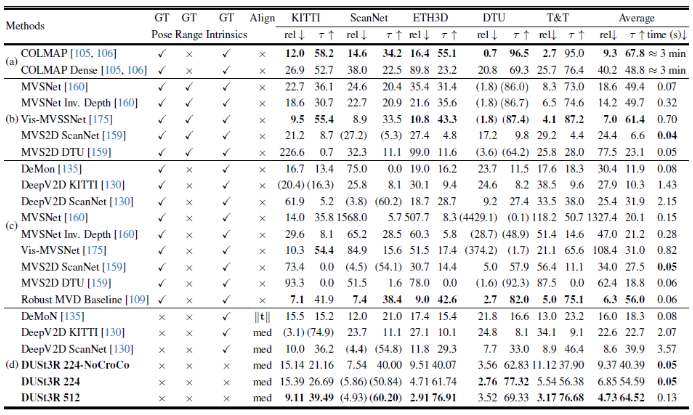
Downstream - Dense 3D reconstruction
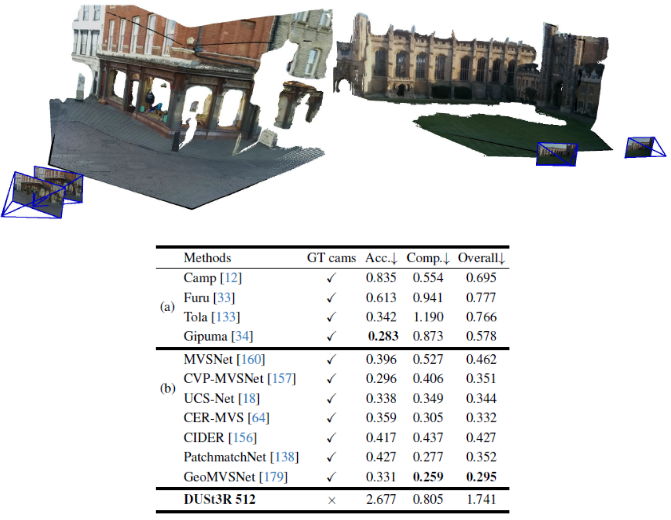
Limitation
- 장점 :
- camera pose 정보 또는 SfM 없어도 self-supervised 방식으로 여러 downstream task 수행 가능
- 원형 호수 파라노마처럼 돌면서 찍을 경우 view에 따라 큰 차이가 없어서 COLMAP은 잘 못 하는데 DUSt3R는 그래도 괜찮
- RGB-based라서 LiDAR가 못 잡는 투명한 물체도 잘 잡음
- 한계 :
- 각 downstream task에서 SOTA 급은 아님.
왜냐하면 regression 방식으로 정확하게 3D recon.하려면 depth가 엄청 정밀해야 하는데 그렇지 않고,
regression 방식이라 COLMAP 방식보다는 오차가 있음.
그래도 pose 없이 높은 성능 이뤘다는 데에 의미가 있음
- 각 downstream task에서 SOTA 급은 아님.