Deblurring 3D Gaussian Splatting
ECCV 2024
Deblurring 3D Gaussian Splatting (ECCV 2024)
Byeonghyeon Lee, Howoong Lee, Xiangyu Sun, Usman Ali, Eunbyung Park
paper :
https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.00834
project website :
https://benhenryl.github.io/Deblurring-3D-Gaussian-Splatting/
code :
https://github.com/benhenryL/Deblurring-3D-Gaussian-Splatting
핵심 :
- defocus blur 구현 :
MLP로 covariance(rotation, scaling)의 변화량을 모델링해서
covariance를 키워서
defocus-blurred image 얻음- camera motion blur 구현 :
MLP로 position 및 covariance의 변화량을 모델링해서
M개의 3DGS sets를 만든 뒤
이걸로 만든 M개의 sharp imgs를 average해서
camera-motion-blurred image 얻음- 위의 MLP를 training에서만 사용하므로
still real-time rendering at inference- sparse point clouds 보상하기 위해 points 추가
또한 먼 거리에 있는 3DGS는 덜 prune out
Introduction
- 3DGS :
- novel-view로 inference할 때
NeRF는 새로운 각도를 MLP에 넣어야만 color, opacity 얻을 수 있지만
3DGS는 spherical harmonics, explicit 기법이라 새로운 각도에 대해서도 바로 color, opacity 얻을 수 있어서
volume rendering이 빠름 - differentiable splatting-based rasterization with parallelism
- novel-view로 inference할 때
- 본 논문 :
- 핵심 :
- 각 3DGS의
covariance를 수정하여blur(adjacent pixels의 혼합)를 모델링하는 작은 MLP사용 - training 시에는 MLP output 곱해서 blurry image를 생성하고
inference 시에는 MLP 사용하지 않아서 real-time으로 sharp image 생성
- 각 3DGS의
- 문제 :
- 3DGS는 initial point cloud에 많이 의존하는데
given images가blurry하면 SfM은 유효한 feature를 식별하지 못해서매우 적은 수의 pointcloud를 추출함 - 심지어 depth가 크면 SfM은 맨 끝에 있는 점을 거의 추출하지 않음
- 3DGS는 initial point cloud에 많이 의존하는데
- 해결 :
- sparse point cloud를 방지하고자
N-nearest-neighbor interpolation으로 points 추가 - 먼 거리의 평면에 많은 Gaussian을 유지하기 위해
위치에 따라 Gaussian pruning
- sparse point cloud를 방지하고자
- contribution :
SOTA qualtiy인데 훨씬 빠른 rendering speed (\(\gt 200\) FPS)
- 핵심 :
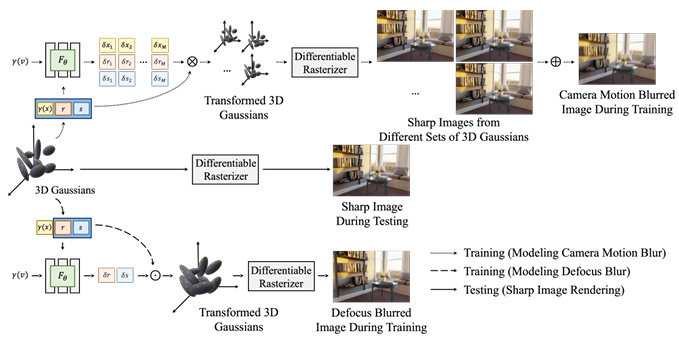
Related Works
- Image Deblurring :
- \(g(x) = \sum_{s \in S_{h}} h(x, s) f(x) + n(x)\)
where \(g(x)\) : blurry image and \(f(x)\) : latent sharp image
where \(h(x, s)\) : blur kernel or PSF (Point Spread Function)
where \(n(x)\) : additive white Gaussian noise (occurs in nature images) - 지금까지 2D image deblurring은 많이 연구되어 왔는데
3D scene deblurring은 3D view consistency 부족 때문에 연구하기 어려웠음
- \(g(x) = \sum_{s \in S_{h}} h(x, s) f(x) + n(x)\)
- Fast NeRF :
- 방법 1)
use additional data-structure to reduce the size and number of MLP layers
but, fail to reach real-time view synthesis- grid-based :
Hexplane, TensoRF, K-planes, Mip-grid, Masked wavelet representation, Direct voxel grid optimization, F2-nerf - hash-based :
InstantNGP, Zip-nerf
- grid-based :
- 방법 2)
trained param.을 faster representation으로 bake해서 real-time rendering- Baking neural radiance fields, Merf, Bakedsdf
- 방법 1)
- Deblurring NeRF :
- DoF-NeRF
[1] :- 단점 :
train하기 위해 all-in-focus image와 blurry image 모두 필요
(all-in-focus image : 화면 전체가 초점이 맞춰져 있는 image)
- 단점 :
- Deblur-NeRF
[2] :- 장점 :
train할 때 all-in-focus image 필요 없음 - 핵심 :
additional small MLP 사용해서
per-pixel blur kernel 예측
- 장점 :
- DP-NeRF
[3] and PDRF[4] :- Deblur-NeRF 발전시킴
- Hybrid
[5] and Sharp-NeRF[6] and BAD-NeRF[7] :- camera motion blur와 defocus blur 중 하나만 다룸
- DoF-NeRF
- Deblurring NeRF 요약 :
- deblur task 잘 수행하지만
NeRF 자체가 rendering time이 오래 걸림
\(\rightarrow\)
real-time differentiable rasterizer 이용하는
3DGS로 deblur task 수행하자!
- deblur task 잘 수행하지만
Background
-
3DGS Link 참고
-
Blur :
- Defocus Blur :
렌즈의초점이 맞지 않아서흐려진 경우
e.g. 인물 사진에서 인물만 초점이 맞고 배경은 흐릿한 경우 - Camera Motion Blur :
셔터가 열려 있는 동안 카메라가 움직이거나 피사체가움직여서흐려진 경우
e.g. 달리는 자동차를 촬영한 경우
- Defocus Blur :
Defocus Blur
- Motivation :
- Defocus Blur는 일반적으로
실제 image와 PSF(point spread func.)(2D Gaussian function) 간의
convolution으로 모델링
즉, a pixel이 주위 pixels에 영향을 미칠 경우 blur - 여기서 영감을 받아
covariance(크기)가 큰 3DGS는 Blur를 유발하고
covariance(크기)가 작은 3DGS는 Sharpimage에 기여한다고 가정
(covariance(dispersion)가 클수록 Gaussian이 더 많은 pixels에 걸쳐 있으니까
더 많은 이웃한 pixels 간의 interference 표현 가능) - 그렇다면 covariance \(\Sigma = R S S^{T} R^{T}\) 를 변경하여 Blur를 모델링해야겠다!
- Defocus Blur는 일반적으로
- Defocus Blur를 모델링하는 MLP :
\((\delta r_{j}, \delta s_{j}) = F_{\theta}(\gamma(x_{j}), r_{j}, s_{j}, \gamma(v))\)
where input : \(j\)-th Gaussian’s position, rotation, scale, view-direction
where output : \(j\)-th Gaussian’s rotation change, scale change
(\(\gamma\) : positional encoding)- transformed 3DGS :
- rotation quaternion : \(\hat r_{j} = r_{j} \cdot \text{min}(1.0, \lambda_{s} \delta r_{j} + (1 - \lambda_{s}))\)
- scaling : \(\hat s_{j} = s_{j} \cdot \text{min}(1.0, \lambda_{s} \delta s_{j} + (1 - \lambda_{s}))\)
- \(\cdot\) : element-wise multiplication
- \(\lambda_{s}\) 로 scale하고 \((1 - \lambda_{s})\) 로 shift : for optimization stability
??? - rotation 및 scaling 변화량의
최솟값을 1로 clip:
\(\hat s_{j} \geq s_{j}\) 이므로 transformed 3DGS는더 큰 covariance를 가져서
Defocus Blur의 근본 원인인 주변 정보의 interference을 모델링할 수 있게 됨
- inference :
scaling factor로 covariance 변화시키는 게 blur kernel의 역할을 하므로
training시에는transformed 3DGS가blurryimage를 생성하지만
inference시에는 MLP를 사용하지 않은기존 3DGS가sharpimage를 생성
\(\rightarrow\)
training할 때는 MLP forwarding과 간단한 element-wise multiplication만 추가 비용이고,
inference할 때는 MLP를 사용하지 않아 Vanilla-3DGS와 모든 단계가 동일하므로
추가 비용 없이 real-time rendering가능
- transformed 3DGS :
Selective Blurring
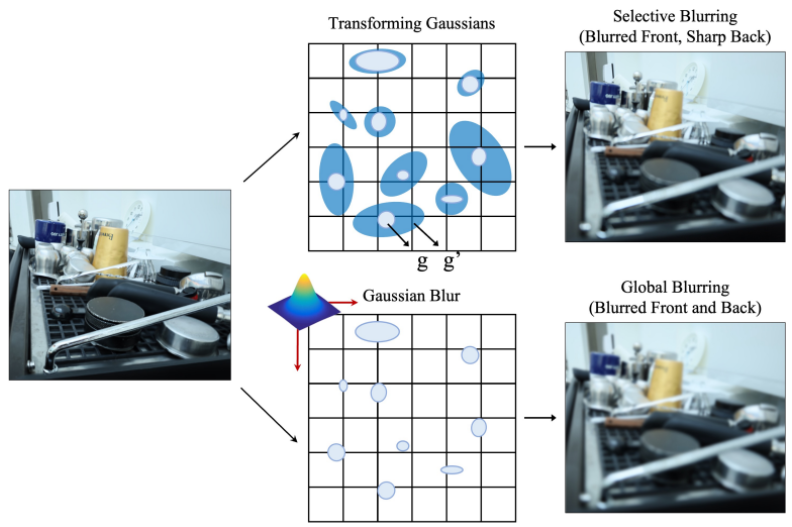
- 초점에 의한 Defocus Blur는
영역마다 흐린 수준이 다름
본 논문에서는각 3DGS마다다르게 \(\delta_{r}, \delta_{s}\) 를 추정하므로
Gaussian의 covariance를 선택적으로 확대시킬 수 있어서
영역에 따라 다르게 blurring 할 수 있으므로
pixel 단위의 blurring을 보다 유연하게 모델링 가능- defocus blur가 심한 영역에 있는 3DGS는 \(\delta_{s}\) 가 더 크도록
- 당연히 단일 유형의 Gaussian Blur kernel을 써서 평균 blurring을 모델링하는 것보다
본 논문에서처럼 3DGS마다 다른 Blur kernel을 적용하여 pixel 단위 blurring을 모델링하는 게 더 좋음!
Camera motion Blur
-
셔터가 열려 있는 exposure time 동안
camera movement가 있으면
light intensities from multipe sources가 inter-mixed되어
Camera motion Blur 발생 -
Camera motion Blur를 모델링하는 MLP :
\({(\delta x_{j}^{(i)}, \delta r_{j}^{(i)}, \delta s_{j}^{(i)})}_{i=1}^{M} = F_{\theta}(\gamma(x_{j}), r_{j}, s_{j}, \gamma(v))\)- transformed 3DGS :
- 3D position : \(\hat x_{j}^{(i)} = x_{j} + \lambda_{p} \delta x_{j}^{(i)}\) (shift)
- rotation quaternion : \(\hat r_{j}^{(i)} = r_{j} \cdot \delta r_{j}^{(i)}\) (element-wise multiplication)
- scaling : \(\hat s_{j}^{(i)} = s_{j} \cdot \delta s_{j}^{(i)}\) (element-wise multiplication)
- Camera motion Blur의 경우
Defocus Blur와 달리 covariance를 무조건 키워야 되는 게 아니므로
min-clip by 1.0 없음
- Camera motion Blur의 경우
- Camera motion Blur :
\(I_{b} = \frac{1}{M} \sum_{i=1}^{M} I_{i}\)- 셔터가 열려 있는 동안 카메라가 움직이는 각 discrete moment는
각 3DGS set에 대응됨 - \(j\)-th Gaussian 의
camera movement를 나타내기 위해
M개의 auxiliary 3DGS sets만들어서
M개의 clean imagesrendering해서
average해서 camera-motion-blurred image 얻음
- 셔터가 열려 있는 동안 카메라가 움직이는 각 discrete moment는
- inference :
마찬가지로inference시에는 MLP를 사용하지 않은기존 3DGS가 clean image를 생성
\(\rightarrow\)
inference할 때는 MLP로 \(M\)-개의 3DGS sets 만들지 않고
Vanilla-3DGS와 모든 단계가 동일하므로
추가 비용 없이 real-time rendering가능
- transformed 3DGS :
Compensation for Sparse Point Cloud
-
문제 1)
3DGS는 initial point cloud에 많이 의존하는데
given input multi-view images가blurry하면
SfM은 유효한 feature를 식별하지 못해서
매우 적은 수의sparse point cloud를 추출함 -
해결 :
- sparse point cloud를 방지하고자
\(N_{st}\) iter. 후에 \(N_{p}\)-개의 points를 uniform \(U(\alpha, \beta)\) 에서 sampling하여 추가
where \(\alpha\) : 기존 point cloud 위치의 최솟값
where \(\beta\) : 기존 point cloud 위치의 최댓값 - 새로운 point의
색상은 KNN(K-Nearest-Neighbor) interpolation으로 할당 - 새로운 points를 uniform 분포에서 sampling해서
빈 공간에 불필요한 points가 생길 수 있으므로
nearest neighbor까지의 거리가 threshold \(t_{d}\) 를 초과하는 points는폐기
- sparse point cloud를 방지하고자

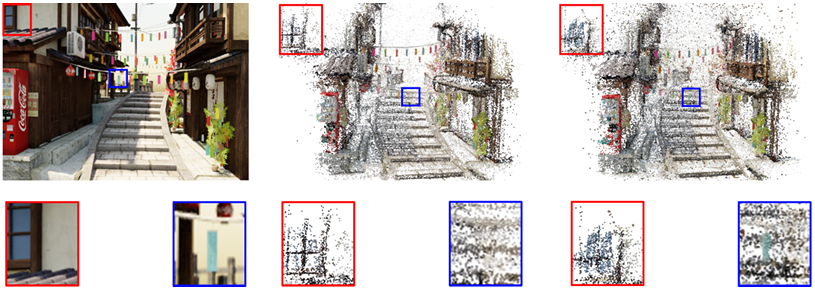
-
문제 2)
심지어 depth of field가 크면
SfM은 맨 끝에 있는 점을 거의 추출하지 않음 -
해결 :
Deblur-NeRF dataset은 forward-facing scene으로만 구성되어 있으므로
dataset에 기록된z-axis 값은relative depthfrom any viewpoint라고 볼 수 있음- 방법 1) 먼 거리에 있는 3DGS 수 늘리기
먼 거리의 평면에 있는 3DGS에 대해 denisfy
\(\rightarrow\)
과도한 densification은 Blur 모델링을 방해하고 추가 계산 비용 필요 - 방법 2)
먼 거리에 있는 3DGS는 덜 prune out
pruning threshold를 깊이에 따라 다르게 scaling
as \(t_{p}, 0.9 t_{p}, \cdots , \frac{1}{w_{p}} t_{p}\)
(먼 거리의 3DGS일수록 낮은 threshold)
\(\rightarrow\)
real-time rendering을 고려했을 때
유연한 pruning으로도 먼 거리의 3DGS sparsity를 보상하기에 충분하다는 걸 경험적으로 발견
- 방법 1) 먼 거리에 있는 3DGS 수 늘리기
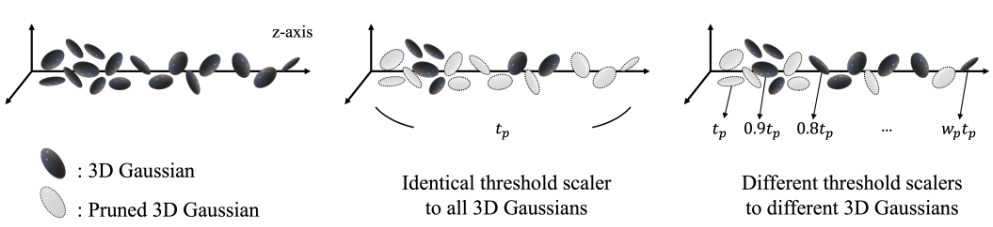
Experiment
- Setting :
- dataset : Deblur-NeRF dataset
- have both synthetic and real images
- has camera motion blur or defocus blur
- GPU : NVIDIA RTX 4090 GPU (24GB)
- optimzier : Adam
- iter. : \(20,000\)
- Blur를 모델링하는 small MLP :
- lr : \(1e^{-3}\)
- hidden layer : 4
- 3 layers : shared
- 1 layer : head for each \(\delta\)
- hidden unit : 64
- activation : ReLU
- initialization : Xavier
- scaling factor for \(\delta\) : \(\lambda_{s}, \lambda_{p} = 1 e^{-2}\)
- sparse point cloud를 보상하기 위해
- \(N_{st} = 2,500\) iter. 후에 \(N_{p}\) 개의 point 추가
\(N_{p}\) 는 기존 point cloud 규모에 비례하며 최대 200,000개 - 색상은 \(K = 4\) 의 KNN interpolation으로 할당
- nearest neighbor까지의 거리가 \(t_{d} = 2\) 을 초과하는 point는 폐기
- \(N_{st} = 2,500\) iter. 후에 \(N_{p}\) 개의 point 추가
- 먼 거리에 있는 3DGS는 덜 pruning하기 위해
pruning threshold를 깊이에 따라 다르게 scaling- pruning threshold \(t_{p} = 5 e^{-3}\) and densification threshold \(2 e^{-4}\)
for real defocus blur dataset - pruning threshold \(t_{p} = 1 e^{-2}\) and densification threshold \(5 e^{-4}\)
for real camera motion blur dataset - pruning threshold multiplier \(w_{p} = 3\)
- pruning threshold \(t_{p} = 5 e^{-3}\) and densification threshold \(2 e^{-4}\)
- camera motion blur를 구현하기 위해
\(M = 5\) 개의 3DGS sets 만들어서
\(M = 5\) 개의 clean images를 average
- dataset : Deblur-NeRF dataset
Results
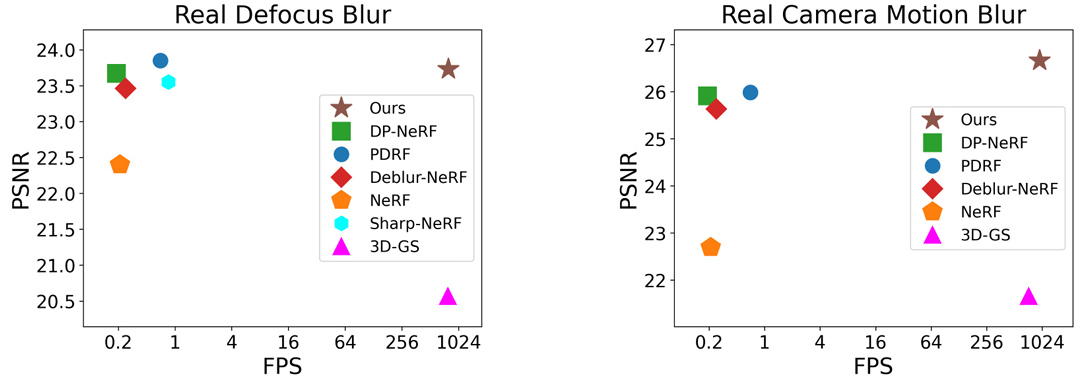
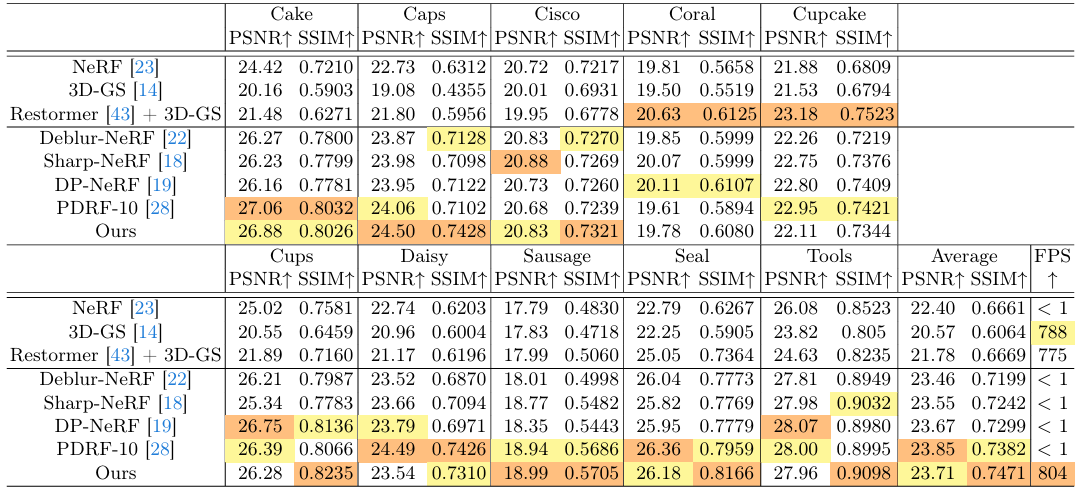
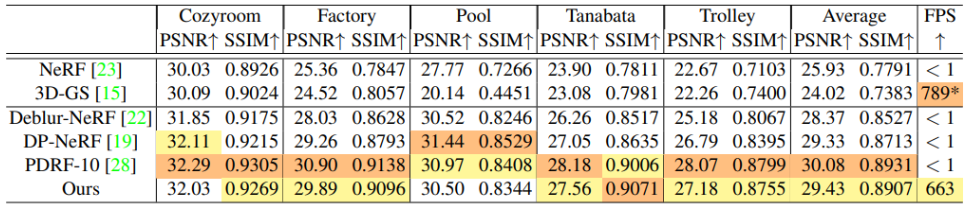
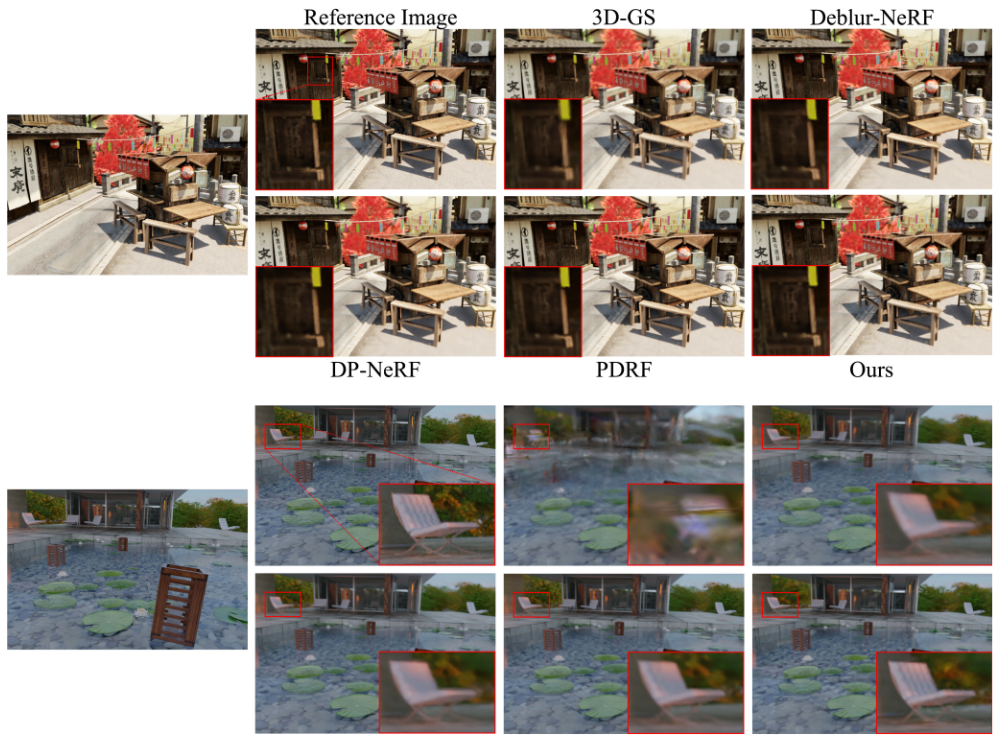
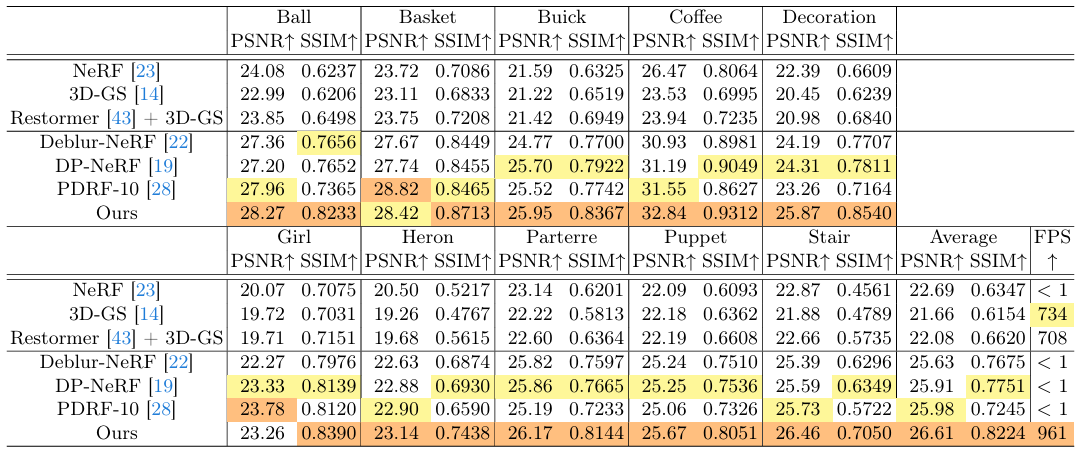
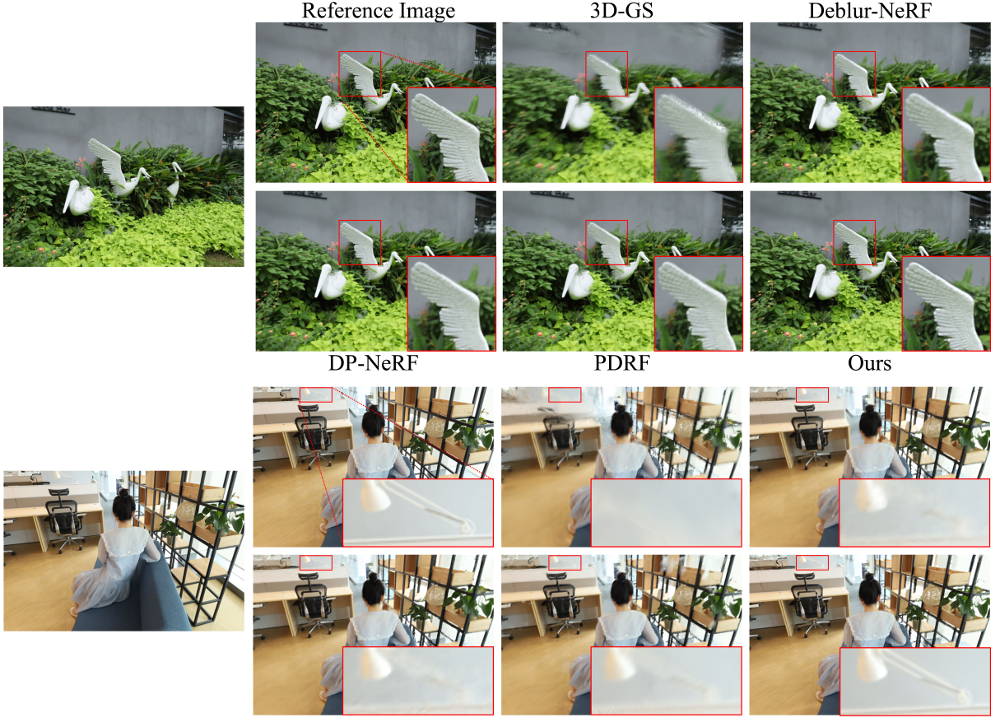
- Results :
-
SOTA deblurring NeRF만큼PSNR높음 -
3DGS만큼FPS높음 - 비교 대상으로 쓰인 논문들 :
- Deblur-NeRF, Sharp-NeRF, DP-NeRF, PDRF
- original 3DGS
- Restormer로 input training images 먼저 deblur한 뒤 original 3DGS
-
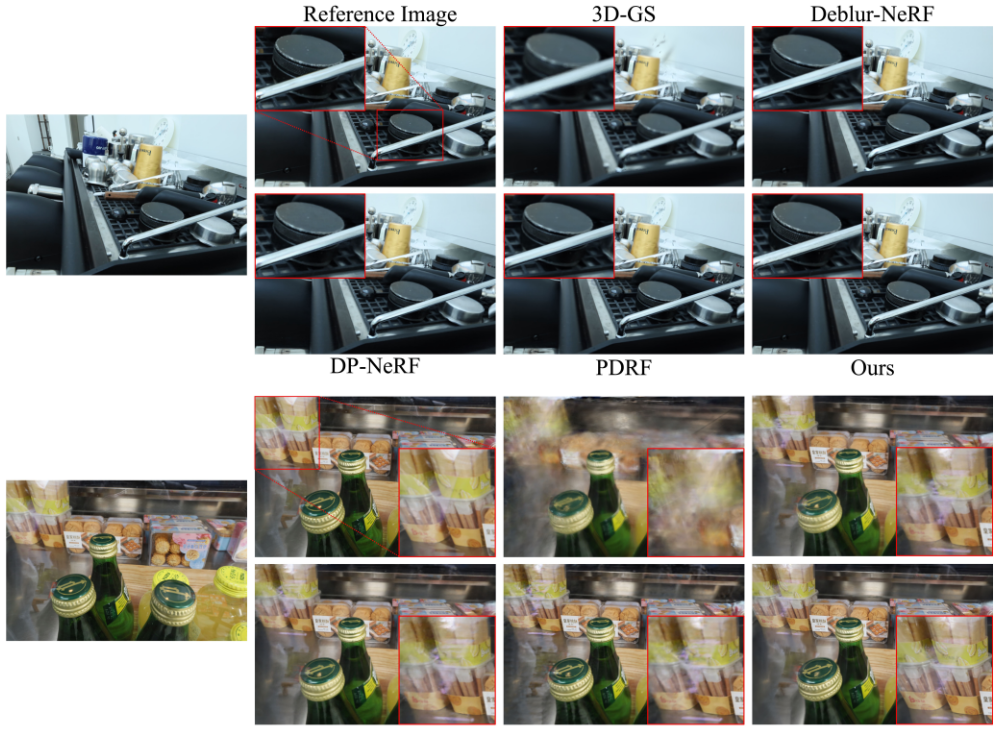

Ablation Study
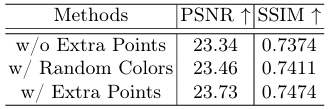
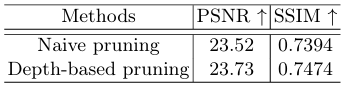
- Ablation Study :
- Extra points allocation
- Depth-based pruning
Limitation and Future Work
- Limitation :
- volumetric rendering 기반의 NeRF-based deblurring 기법들을
rasterization 기반의 3DGS에 적용하기 어렵
\(\rightarrow\)
MLP로world-space에서의 rays 또는 kernels를 변형하는 대신
MLP로rasterized image space에서의 kernels를 변형하면
Deblurring 3DGS 구현 가능
\(\rightarrow\)
하지만 kernel interpolation 방향으로 가면
pixel interpolation은 추가 비용이 발생하며
3DGS의 geometry를 implicitly 변형하는 것일 뿐이므로
해당 방법은 3DGS로 blur를 모델링하는 최적의 방법이 아닐 것이다
이를 개선하기 위한 future works 필요
- volumetric rendering 기반의 NeRF-based deblurring 기법들을
Code Review
- blur kernel 함수 :
Defocus Blur 및 Camera motion Blur - sparse point cloud 보상하기 위해 add points :
Question
-
Q1 :
small MLP는 어떤 architecture로 구성되어 있나요?
Dust3R 기반의 논문들을 보면
transformer 등 pre-trained complex model 가져와서 쓰는데
feed-forward 방식으로 학습하므로
빠르면서도 성능이 좋습니다. 이를 적용할 수 있지 않을까요? -
A1 :
일단 본 논문에서는 fast training 유지하기 위해 shallow MLP가 simply fc layers로 구성되어 있습니다
말씀해주신대로 simple shallow MLP 대신 더 좋은 network 쓰면 성능이 더 좋아질 것 같다고 생각하는데,
deblurring task를 다룬 본 논문 이후의 논문들을 아직 읽어보지 않아서
혹시 읽어보고 좋은 아이디어 있다면 공유하도록 하겠습니다. -
Q2 :
본 논문이 deblurring task를 위해 pre-trained 3DGS를 가져와서 fine-tuning하는 것인가요? -
A2 :
아닙니다. 기존 3DGS에 blur를 모델링하는 MLP만 추가해서 scratch부터 training하고,
이로써 input image가 더러워도(blurry하더라도) clean image를 rendering할 수 있게 됩니다.
그리고 기존 3DGS와 같이 per-scene 방식으로 학습하는 것으로 알고 있습니다. -
Q3 :
blurry input image를 dataset에서 미리 빼버리면 deblurring을 해야 하는 상황이 없어지잖아요
이처럼 제가 생각하기에는 굳이 deblurring을 해야 하나 라는 생각이 듭니다. -
A3 :
일단 deblurring이라는 게 super-resolution처럼 하나의 task로 생각할 수 있습니다
input image가 blurry 할 수 있는데 말씀해주신대로 이를 dataset에서 미리 뺀다는 것 자체가 manual effort를 필요로 합니다 (이를 model이 대신 해준다면 좋겠죠)
그리고 만약 주어진 모델이 deblurring을 수행할 수 있다면 다른 모델의 앞단에 쓰여서 blur를 제거하는 pre-processing 용도로도 쓰일 수 있습니다.
이로써 input images가 현실에서 있을 법한 더러운(blurry) 이미지더라도 상관 없이 input으로 쓸 수 있습니다.
2D image 또는 video를 deblurring하는 논문들은 이미 많이 있는데
3D scene deblurring의 경우에는 3D view consistency 때문에 어려움이 있었습니다.
그러다가 3DGS 등장 이후로 처음 3DGS deblurring을 시도한 논문이 본 논문이라고 보시면 될 것 같습니다. -
Q4 :
그렇다면 deblurring task라는 게 uncertainty를 해결하는 것이라고 볼 수 있을까요? 아니면 이것과는 별개의 task로 봐야 할까요? -
A4 :
(3D recon. 및 novel view synthesis에서 uncertainty라는 용어가 자주 등장하는데, 관련 논문들을 아직 많이 읽어보지 않아서 확실하게 답변드리지 못하겠습니다.) -
Q5 :
dataset에 있는 image들이 blurry하지 않고 clean(sharp) 하더라도
camera explore 하면서 novel view에 대해 rendering을 하다보면 rendered image에 blur가 생길 수 있을 것 같은데
deblurring이라는 게 이러한 blur도 제거해주나요? -
A5 :
일단 본 논문에서 deblur를 하는 원리는 covariance를 조정하는 MLP로 blur를 모델링하여
해당 MLP(blur 담당)를 사용하지 않는 inference에서는 deblurred image가 rendering되는 것입니다
하지만 input이 blurry해서 생긴 blur가 아니라 rendering하다보니 생기는 artifacts로서의 blur의 경우라면
해당 MLP가 artifacts로서의 blur도 잘 모델링해줄지는 모르겠습니다. 더 찾아봐야 할 것 같습니다. -
Q6 :
혹시 본 논문을 읽으면서 생각해보셨던 limitation이 있을까요? 논문에 적혀있는 것 말고 개인적인 생각이 있으신지 궁금합니다.
저는 뭔가 본 논문의 알고리즘이 artificial하다는 생각이 들었습니다. -
A6 :
(개인적으로 생각해본 limitation 답변 못 드림 ㅠㅠ 앞으로는 논문 읽을 때 novelty 말고도 limitation이 무엇일지 생각하는 습관 길러보자!)
기존 deblur nerf에서는 deblur kernel을 이용해서 여러 ray를 쏴서 2D 상에서 pixel들을 interpolate해서 blur를 모델링하는데
deblurring 3DGS에서는 3D 상에서 Gaussian covariance를 키우는 방식으로 interpolate를 비슷하게 구현했다는 논리(가정)이고
결과적으로 성능이 좋게 나왔으니 본인들 주장(가정)이 맞았다 인 것 같아서 말씀해주신대로 artificial한 느낌이 들긴 하네요