Solar LLM with Langchain
Upstage Solar LLM as Personalized LLM
Solar LLM by Upstage
Solar LLM as Personalized LLM
-
Referenced Github :
UpstageAI-cookbook
UpstageAI-cookbook
OracleDB-cookbook -
Solar mini LLM :
small-size
best LLM for fine-tuning
can be used as personalized LLM -
Future of AI Ecosystem Hierarchy :
Domain-specific and self-fine-tuned LLMs
Solar LLM O/S
O/S
AI chips -
Langchain :
LLM과 application의 통합을 간소화하는 SDK -
핵심 기능 : 앞으로 아래에서 배울 예정!!
- LLM 사용 (query, context)
- Groundedness Check (팩트체크)
- Layout Analyzer (PDF 또는 img에서 정보 추출)
- Embedding and DB vector store (embedding vector를 DB에 저장)
- Define Custom Tools (img 생성, 뉴스 검색, 스케쥴 관리 등)
Chat
from langchain_upstage import ChatUpstage
llm = ChatUpstage()
llm.invoke("What's the best season to get to Korean?") # invoke llm
llm = ChatUpstage(model="solar-1-mini-chat-ja")
llm.invoke("ソーラーLLM、こんにちは。ソーラーLLM、こんにちは。")
Few-shot Learning - Chain
# 1. use Chat Prompt Template
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
# 2. 농담조로 말하도록 Few-shot Learning
chat_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", "You are a helpful assistant."),
("human", "What is the capital of France?"),
("ai", "I know of it. It's Paris!!"),
("human", "What about Korea?"),
]
)
# 3. define and invoke chain
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
chain = chat_prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
chain.invoke({})
# 1. use Prompt Template
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
# 2. 한 번에 답을 내도록 (Standard Prompting) Few-shot Learning
# 한 번에 답을 내려다보니 llm이 답 틀리게 내놓음
prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template(
"""
Q: Roger has 5 tennis balls. He buys 2 more cans of tennis balls. Each can has 3 tennis balls. How many tennis balls does he have now?
A: The answer is 11.
Q: The cafeteria had 23 apples. If they used 20 to make lunch and bought 6 more, how many apples do they have?
A: the answer is
"""
)
# 3. define and invoke chain
chain = prompt_template | llm | StrOutputParser()
chain.invoke({})
# 1. use Prompt Template
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
# 2. 설명하면서 답을 내도록 (Chain-of-Thought Prompting) Few-shot Learning
# 설명하면서 답을 내니 llm이 알맞게 답을 내놓음
prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template(
"""
Q: Roger has 5 tennis balls. He buys 2 more cans of tennis balls. Each can has 3 tennis balls. How many tennis balls does he have now?
A: Roger started with 5 balls. 2 cans of 3 tennis balls
each is 6 tennis balls. 5 + 6 = 11. The answer is 11.
Q: The cafeteria had 23 apples. If they used 20 to make lunch and bought 6 more, how many apples do they have?"""
)
# 3. define and invoke chain
chain = prompt_template | llm | StrOutputParser()
chain.invoke({})
Zero-shot Learning - Chain
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
# Zero-shot, 즉 예시를 주지 않고
# "Let's think step by step"이라는 마법의 한 문장만 써줬는데도
# 답 잘 내놓음
prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template(
"""
Q: Roger has 5 tennis balls. He buys 2 more cans of tennis balls. Each can has 3 tennis balls. How many tennis balls does he have now?
A: The answer is 11.
Q: The cafeteria had 23 apples. If they used 20 to make lunch and bought 6 more, how many apples do they have?
A: Let's think step by step.
"""
)
chain = prompt_template | llm | StrOutputParser()
chain.invoke({})
Divide-and-Conquer
- Please provide three questions from the following text
보다는
- Please extract three keywords from the following text 한 다음
Please provide one question from the following text regarding “Depth up-scaling (DUS)”
Prompt 반복
python f-string과 비슷한 원리
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template(
"Tell me a {adjective} joke about {content}."
)
# prompt_template.format(adjective="funny", content="chickens")
chain = prompt_template | llm | StrOutputParser()
chain.invoke({"adjective": "funny", "content": "chickens"})
Keep Message History in LangChain Prompts
MessagesPlaceholder
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
# General Chat form with Message History
rag_with_history_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", "You are a helpful assistant."),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="history"),
("human", "{input}"),
]
)
from langchain_core.messages import AIMessage, HumanMessage
# Message History argument
history = [
HumanMessage("What is the capital of France?"),
AIMessage("It's Paris!!"),
]
chain = rag_with_history_prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
chain_result = chain.invoke({"history": history, "input": "What about Korea?"})
print(chain_result)
Groundedness Check with LangChain
Groundedness Check :
답(answer)이 주어진 문맥(context)과 일맥상통하는지 (구라가 아닌지) 팩트 체크!
from langchain_upstage import UpstageGroundednessCheck
groundedness_check = UpstageGroundednessCheck()
answer = chain.invoke(
{
"question": "What is DUS?",
"Context": context,
}
)
print("Potential answer: ", answer)
gc_result = groundedness_check.invoke({"context": context, "answer": answer})
print("GC check result: ", gc_result)
if gc_result.lower().startswith("grounded"):
print("Groundedness check passed")
else:
print("Groundedness check failed")
PDF Loader (Context로 사용)
PDF에 있는 내용을 읽어와서 Context로 사용!
from langchain_community.document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
loader = PyPDFLoader("pdfs/solar_sample.pdf")
docs = loader.load() # or layzer.lazy_load()
print(docs[0].page_content[:1000])
Layout Analyzer (Context로 사용)
LLM이 받아들이기 좋은 형태로 문서를 읽기 위해
Extract layouts, tables, and figures from any document to .html file
Maximize RAG performance (RAG는 이후에 설명 예정)
! pip3 install -qU markdownify langchain-upstage requests
import os
from langchain_upstage import UpstageLayoutAnalysisLoader
from IPython.display import display, HTML
os.environ["UPSTAGE_API_KEY"] = "UPSTAGE_API_KEY"
loader = UpstageLayoutAnalysisLoader("invoicem.PNG", split="page", use_ocr=True)
# For improved memory efficiency, consider using the lazy_load method to load documents page by page.
pages = loader.load() # or loader.lazy_load()
for page in pages:
print(page)
loader = UpstageLayoutAnalysisLoader("pdfs/solar_sample.pdf", output_type="html")
docs = layzer.load() # or loader.lazy_load()
display(HTML(docs[0].page_content[:5000]))
RAG: Retrieval Augmented Generation
- RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) :
-
pdf, html 등 주어진 파일에서 query와 관련 있는 부분만 검색해서 context로서 사용! - Large language models (LLMs) have a limited context size
- Not all context is relevant to a given question
-
Relevant context is retrieved(검색) from external data sourcesand added to the prompt - LLM generates a response based on this augmented context prompt
- RAG is particularly useful for Question Answering on custom datasets
- Query \(\rightarrow\) Retrieve (Search) \(\rightarrow\) Augmented Prompt \(\rightarrow\) LLM \(\rightarrow\) Answer
-
- Chunking, Splitting :
- Fixed-size chunking : split text into equal-sized chunks based on character or token count
- Semantic chunking : split text based on semantic boundaries like sentences, paragraphs, or sections
- Hierarchical chunking : create chunks at multiple levels of granularity (The ideal chunk size depends on the embedding model, retrieval use-case, and downstream task)
from langchain_upstage import UpstageLayoutAnalysisLoader
from langchain_community.retrievers import BM25Retriever
from langchain_text_splitters import (
Language,
RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter,
)
layzer = UpstageLayoutAnalysisLoader(
"pdfs/kim-tse-2008.pdf", use_ocr=True, output_type="html"
)
docs = layzer.load()
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.from_language(
chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=100, language=Language.HTML
)
splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs)
retriever = BM25Retriever.from_documents(splits)
query = "What is bug classficiation?"
context_docs = retriever.invoke("bug") # keyword search
chain.invoke({"question": query, "Context": context_docs})
Keyword Search 대신 Semantic Search with Embedding space
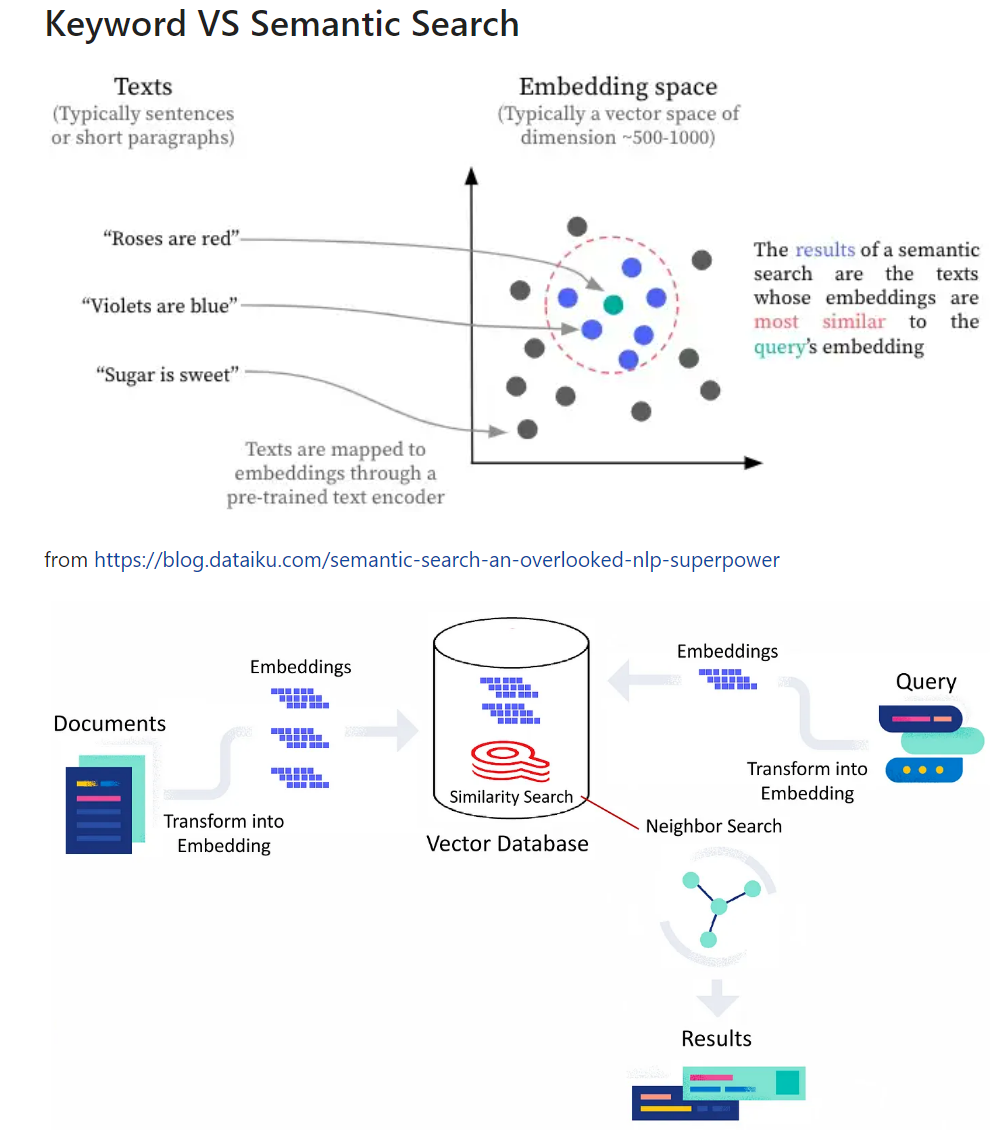
Solar-Embedding-1-Large (v1.0)
Convert unstructured text data into embedding vectors
from langchain_upstage import UpstageEmbeddings
from langchain_chroma import Chroma
from langchain_upstage import UpstageEmbeddings
from langchain.docstore.document import Document
embeddings_model = UpstageEmbeddings(
api_key="UPSTAGE_API_KEY",
model="solar-embedding-1-large"
)
embeddings = embeddings_model.embed_documents(
[
"What is the best season to visit Korea?",
]
)
query_result = embeddings.embed_query("What does Sam do?") # vector
sample_text_list = [
"Korea is a beautiful country to visit in the spring.",
"The best time to visit Korea is in the fall.",
"Best way to find bug is using unit test.",
"Python is a great programming language for beginners.",
"Sung Kim is a great teacher.",
"맛있는 좋은 과일을 많이 먹어 볼까?"
]
sample_docs = [Document(page_content=text) for text in sample_text_list]
vectorstore = Chroma.from_documents(
documents=sample_docs,
embedding=UpstageEmbeddings(model="solar-embedding-1-large"),
)
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
result_docs = retriever.invoke("When to visit Korea?")
print(result_docs[0].page_content[:100])
RAG Summary
- load doc
- chunking, splits
- embedding, indexing (vector store)
- retrieval, augmenting context (find Top-k most similar doc chunks in vector store with the query embedding)
- invoke chain based on the augmented context by retrieval
from langchain_upstage import UpstageLayoutAnalysisLoader
from langchain_text_splitters import (
Language,
RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter,
)
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_upstage import ChatUpstage
# 1. load doc
layzer = UpstageLayoutAnalysisLoader("pdfs/kim-tse-2008.pdf", output_type="html")
docs = layzer.load()
# 2. chunking & splits
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.from_language(
chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=100, language=Language.HTML
)
splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs)
# 3. Embedding & indexing
vectorstore = Chroma.from_documents(
documents=splits,
embedding=UpstageEmbeddings(model="solar-embedding-1-large"),
)
# 4. retrieve
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
result_docs = retriever.invoke("What is Bug Classification?")
print(len(result_docs))
print(result_docs[0].page_content[:100])
# 5. invoke chain based on the augmented context by retrieval
llm = ChatUpstage()
prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template(
"""
Please provide most correct answer from the following context.
If the answer is not present in the context, please write "The information is not present in the context."
---
Question: {question}
---
Context: {Context}
"""
)
chain = prompt_template | llm | StrOutputParser()
chain.invoke({"question": "What is bug classficiation?", "Context": result_docs})
Oracle DB를 persistent memory로 쓰기

매번 100만 개의 pdf를 load해서 index할 수는 없는 일!
- load doc
- chunking, splits
- embedding, indexing (
vector store with Oracle DB) - retrieval, augmenting context
- split한 text가 이미 Oracle DB vector store에 있는지 체크
- 없다면 embedding, indexing again
- invoke chain based on the augmented context by retrieval
! pip3 install -qU markdownify langchain-upstage rank_bm25
import oracledb
from langchain_upstage import UpstageLayoutAnalysisLoader
# 0. connect to Oracle DB
username=os.environ["DB_USER"]
password=os.environ["DB_PASSWORD"]
dsn=os.environ["DSN"]
con = oracledb.connect(user=username, password=password, dsn=dsn)
try:
conn23c = oracledb.connect(user=username, password=password, dsn=dsn)
print("Connection successful!", conn23c.version)
except Exception as e:
print("Connection failed!")
# 1. load doc
layzer = UpstageLayoutAnalysisLoader("pdfs/kim-tse-2008.pdf", output_type="html")
docs = layzer.load()
# 2. chunking & splits
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.from_language(
chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=100, language=Language.HTML
)
splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs)
# check if text is in the vector store
def is_in_vectorstore(vectorstore, text):
search_results = vectorstore.get(ids=[text])
if search_results and search_results["ids"]:
return True
else:
return False
# 3. Embedding & indexing 방법 1.
vectorstore = Chroma(
persist_directory="./chroma_db",
embedding_function=UpstageEmbeddings(model="solar-embedding-1-large"),
)
# 3. Embedding & indexing 방법 2.
knowledge_base = OracleVS.from_documents(docs, upstage_embeddings, client=conn23c, table_name="text_embeddings2", distance_strategy=DistanceStrategy.DOT_PRODUCT)
# result_chunks = knowledge_base.similarity_search(user_question)
vectorstore = OracleVS(client=conn23c, embedding_function=upstage_embeddings, table_name="text_embeddings2", distance_strategy=DistanceStrategy.DOT_PRODUCT) # create vector store
oraclevs.create_index(
client=conn23c,
vector_store=vectorstore,
params={
"idx_name": "ivf_idx1",
"idx_type": "IVF",
},
) # index 추가
# 4. retrieve
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
unique_splits = [
split for split in splits if not is_in_vectorstore(vectorstore, split.page_content)
]
print(len(unique_splits))
# 5. split한 text가 이미 Oracle DB vector store에 있는지 체크
# 6. 없다면 embedding, indexing again
if len(unique_splits) > 0:
vectorstore = Chroma.from_documents(
ids=[split.page_content for split in unique_splits],
persist_directory="./chroma_db",
documents=unique_splits,
embedding=UpstageEmbeddings(model="solar-embedding-1-large"),
)
# 7. invoke chain based on the augmented context by retrieval
llm = ChatUpstage()
prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template(
"""
Please provide most correct answer from the following context.
If the answer is not present in the context, please write "The information is not present in the context."
---
Question: {question}
---
Context: {Context}
---
Output: please, response in Korean
"""
)
chain = ({"context": retriever, "question": RunnablePassthrough()} | prompt_template | llm | StrOutputParser())
response = chain.invoke("What is bug classficiation?")
Smart RAG
local vector store에 검색했을 때
- 내가 아는 건
local RAG로 처리 - 내가 모르는 건
external search로 처리
# 주어진 context만으로 주어진 question에 답변할 수 있는지 판단
# RAG or Search?
def is_in(question, context):
is_in_conetxt = """As a helpful assistant,
please use your best judgment to determine if the answer to the question is within the given context.
If the answer is present in the context, please respond with "yes".
If not, please respond with "no".
Only provide "yes" or "no" and avoid including any additional information.
Please do your best. Here is the question and the context:
---
CONTEXT: {context}
---
QUESTION: {question}
---
OUTPUT (yes or no):"""
is_in_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(is_in_conetxt)
chain = is_in_prompt | ChatUpstage() | StrOutputParser()
response = chain.invoke({"context": context, "question": question})
print(response)
return response.lower().startswith("yes")
# Smart RAG, Self-Improving RAG
import os
from tavily import TavilyClient
def smart_rag(question, context):
if not is_in(question, context):
print("Searching in tavily")
tavily = TavilyClient(api_key=os.environ["TAVILY_API_KEY"])
context = tavily.search(query=question)
chain = prompt_template | llm | StrOutputParser()
return chain.invoke({"context": context, "question": question})
smart_rag("What is DUS?", solar_summary)
# 질문에 대한 답변이 solar_summary에 있는 내용이므로 RAG
# yes
# 'The answer to the question "What is DUS?" is:\n\nDepth Up-Scaling (DUS)'
smart_rag("How to get to Seoul from SF?", solar_summary)
# solar_summary에 없는 내용이므로 Search
# no
# Searching in tavily
# 'The answer to "How to get to Seoul from SF?" is:\n\n1. Fly from San Francisco (SFO) to Seoul (ICN) with airlines such as ANA, Japan Airlines, Asiana Airlines, Korean Air, and United Airlines.\n2. Take a train from Incheon Int\'l Airport T1 to Seoul Station.\n3. Take the BART from Civic Center / UN Plaza to Milpitas and then fly from San Jose (SJC) to Incheon (ICN).\n\nPlease note that the cheapest flights from San Francisco to Seoul start at $453 with AIR PREMIA.'
Smart RAG with Tools
- Define
Custom Tools - Create a list of tools
- Bind the tools to LLM
특정 task (산수 계산 혹은 뉴스기사 검색 등) 맞춤형으로
custom tools를 정의함으로써
LLM 답변의 질을 높일 수 있음!
! pip3 install -qU markdownify langchain-upstage rank_bm25
from langchain_core.tools import tool
import requests
import os
from tavily import TavilyClient
# external API to search
tavily = TavilyClient(api_key=os.environ["TAVILY_API_KEY"])
# 1. Define Custom Tools
@tool
def add(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Adds a and b."""
return a + b
@tool
def solar_paper_search(query: str) -> str:
"""Query for research paper about solarllm, dus, llm and general AI.
If the query is about DUS, Upstage, AI related topics, use this.
"""
return solar_summary
@tool
def internet_search(query: str) -> str:
"""This is for query for internet search engine like Google.
Query for general topics.
"""
return tavily.search(query=query)
@tool
def get_news(topic: str) -> str:
"""Get latest news about a topic.
If users are more like recent news, use this.
"""
# https://newsapi.org/v2/everything?q=tesla&from=2024-04-01&sortBy=publishedAt&apiKey=API_KEY
# change this to request news from a real API
news_url = f"https://newsapi.org/v2/everything?q={topic}&apiKey={os.environ['NEWS_API_KEY']}"
respnse = requests.get(news_url)
return respnse.json()
# 2. Create a list of tools
tools = [add, solar_paper_search, internet_search, get_news]
# 3. Bind the tools to LLM
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
llm_with_tools.invoke("What is Solar LLM?").tool_calls
# 출력 : [{'name': 'solar_paper_search', 'args': {'query': 'Solar LLM'}, 'id': 'cb1687d2-7c6a-45dc-8287-19376c335cd4'}]
llm_with_tools.invoke("What's best place in Seoul?").tool_calls
# 출력 : [{'name': 'internet_search', 'args': {'query': 'best place in Seoul'}, 'id': '1f86d563-de15-460a-abc0-0e644e284518'}]
# Smart RAG, Self-Improving RAG
import os
from tavily import TavilyClient
def call_tool_func(tool_call):
tool_name = tool_call["name"].lower()
if tool_name not in globals():
print("Tool not found", tool_name)
return None
selected_tool = globals()[tool_name]
return selected_tool.invoke(tool_call["args"])
def tool_rag(question):
for _ in range(3): # try 3 times
tool_calls = llm_with_tools.invoke(question).tool_calls
if tool_calls:
break
else:
print("try again")
if not tool_calls:
return "I'm sorry, I don't have an answer for that."
print(tool_calls)
context = ""
for tool_call in tool_calls:
context += str(call_tool_func(tool_call))
chain = prompt_template | llm | StrOutputParser()
return chain.invoke({"context": context, "question": question})
tool_rag("What is Solar llm?")
# 출력 : [{'name': 'solar_paper_search', 'args': {'query': 'What is Solar llm?'}, 'id': 'cb291b01-a1aa-4839-84a8-a473f4eb0920'}] 'Solar llm is a large language model (LLM) with 10.7 billion parameters.'
tool_rag("What is news about Tesla?")
# 출력 : [{'name': 'get_news', 'args': {'topic': 'Tesla'}, 'id': 'aade5002-b9e2-4a23-92d7-fd66f12cfeb6'}] "The news about Tesla is that the company has issued a voluntary recall for nearly 4,000 Cybertrucks due to a fault with the accelerator pedal that could get trapped, pushing the car to full speed."
Fine-tuning with Predibase
CFT (Continued Fine-Tuning) : feedback database에 기반하여 계속 fine-tuning
adapter = pb.adapters.create(
config=FinetuningConfig(
base_model = "solar-1-mini-chat-240612",
epochs = 1, # default: 3
rank = 1, # default: 16
),
dataset = pb_dataset, # also accepts the dataset name as str
repo = repo,
description = "initial model with defaults"
)